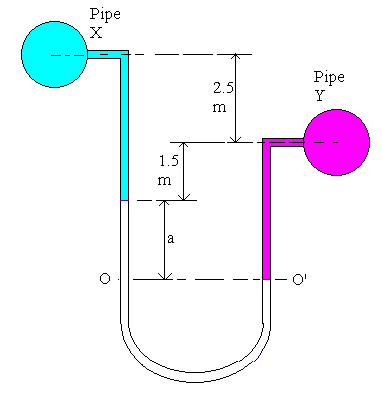
A U - tube differential mercury manometer is connected between two pipes X and Y. Pipe X contains carbon tetra chloride (Sp.gr. 1.59) under a pressure of 103 kN/m2 and pipe Y contains oil (Sp.gr. 0.8) under a pressure of 172 kN/m2. Pipe X is 2.5 m above pipe Y. Mercury level in the limb connected to pipe X is 1.5 m below the centerline of pipe Y. Find the manometer reading as shown by a centimeter scale attached to it.
Data:

Fluid in pipe X = carbon tetra chloride
Density of Carbon tetra chloride = 1.59 x 1000 kg/m3
Px = 103 kN/m2
Fluid in pipe Y= oil
Density of Carbon tetra chloride = 0.8 x 1000 kg/m3
Py = 172 kN/m2
Formula:
P = ρgh
Principle: Pressure at the same level in a continuous body of static fluid is equal.
Calculations:
Equating the pressure at the two legs of the manometer at OO':
For the left hand leg pressure at O = Po = Px + (2.5 + 1.5) x 1590 x 9.812 + a x 13600 x 9.812 N/m2
For the right hand leg pressure at O' = Po' = Py + (1.5 + a) x 800 x 9.812 N/m2
Px + (2.5 + 1.5) x 1590 x 9.812 + a x 13600 x 9.812 = Py + (1.5 + a) x 800 x 9.812
Substituting for Px and Py,
103000 + 62404.32 + 133443.2 x a = 172000 + 7849.6 x a + 11774.4
-18370.08 = - 125593.6 x a
a = 0.146 m = 14.6 cm
Manometer Reading =
14.6 cm of HgLast Modified on: 01-May-2024
Chemical Engineering Learning Resources - msubbu
e-mail: learn[AT]msubbu.academy
www.msubbu.in