For a second order reaction,
XA/(CAo (1- XA) ) = kt
i.e., XA/(1 - XA) vs. t is a straight line
Establish the kinetics of the thermal decomposition of Nitrous oxide from the following data and find the reaction rate at 990oC and an initial pressure of 200 mm Hg.
t, min 20 53 100 % decomposition 23 50 73
Calculations:
Conversion (XA) of Nitrous oxide (A) for various time values are given are given.
We shall test the date for first order, second order kinetics by integral method of analysis.
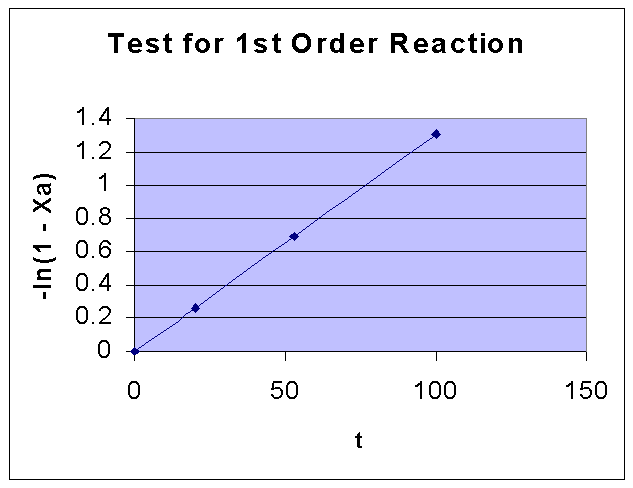
For a first order reaction, -ln(1 - XA) vs. t is a straight line.
t, min 20 53 100 XA 0.23 0.50 0.73
|
t, min |
20 |
53 |
100 |
|
XA |
0.23 |
0.5 |
0.73 |
|
1-XA |
0.77 |
0.5 |
0.27 |
|
-ln(1 - XA) |
0.261365 |
0.693147 |
1.309333 |
From the above data the following graph is drawn:
For a second order reaction, XA/(CAo (1- XA) ) = kt i.e., XA/(1 - XA) vs. t is a straight line
|
t, min |
20 |
53 |
100 |
|
XA/(1 - XA) |
0.298701 |
1 |
2.703704 |
From the above data the following graph is drawn:
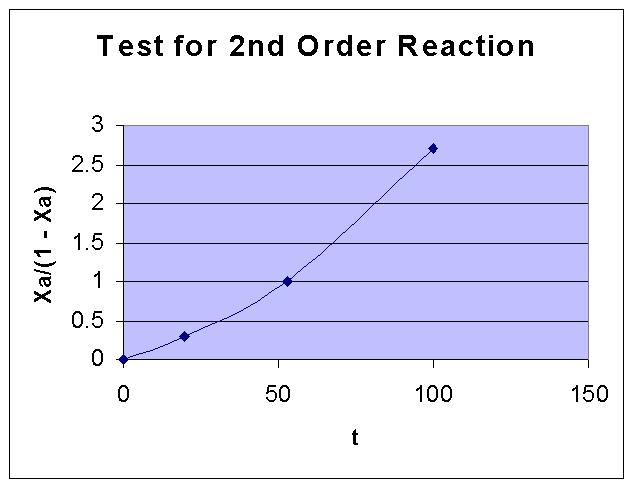
By comparing the two graphs, it can be seen that First order kinetics is well fiiting the given data. Fisrt order rate constant k is obtained from the slope of the first order data graph, and it is = 0.0131 sec-1.
Therefore, -rA = kCA = kCAo(1 - XA) = kpAo(1 - XA)/RT = (1 - XA) x 0.0131 x (200/760) x 101325 /(8314 x (990 + 273)) = 3.327 x 10-5(1 - XA)
i.e., -rA = 3.327 x 10-5(1 - XA)
where XA is fractional decomposition of Nitrous oxide, and -rA is the rate of decomposition of Nitrous oxide.
Last Modified on: 30-Apr-2024
Chemical Engineering Learning Resources - msubbu
e-mail: learn[AT]msubbu.academy
www.msubbu.in