The thermal decomposition of nitrous oxide (N2O) in the gas phase at 1030 K is studied in a constant volume vessel at various initial pressures of N2O. The half-life data so obtained are as follows:
po (mm Hg) 52.5 139 290 360 t1/2 (sec) 860 470 255 212
2N2O -> 2N2 + O2
Determine the rate equation that fits the data.
Calculations:
t1/2 Vs. CAo in a log-log plot is a straight line with a slope of 1-n
CAo = pAo/RT = po/RT (for an ideal gas)
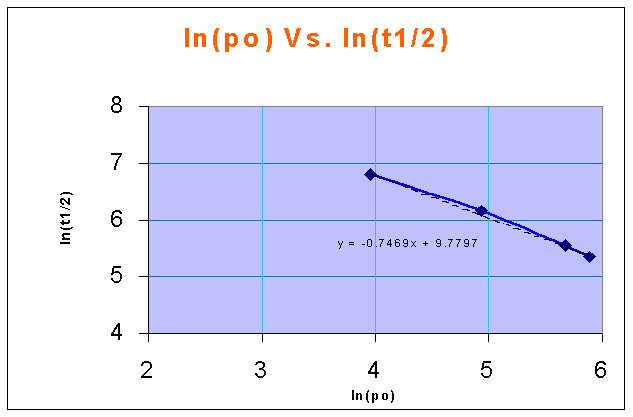
ln(CAo) Vs. ln(t1/2) in a linear XY plot gives a straight line, and the slope of the line is 1 - n

from the above figure,
1-n = -0.7469
therefore, n = 1 + 0.7469 = 1.7469 = 1.75
i.e.,
Order of the reaction (n) = 1.75t1/2 and CAo are related by the formula:
\(\displaystyle t_{1/2} = \frac{2^{n-1}-1}{k(n-1)}C_{Ao}^{1-n} \)
for a value of po = 290, and t1/2 = 255,
CAo = (290/760) x 1.01325 x 10-5/(8314 x 1030) = 4.515 x 10-3 gmol/lit.
therefore,
k = (21.75 - 1 - 1) x (4.515 x 10-3)(1-1.75) / (255 x (1.75 - 1)) = 0.2046 sec-1.(gmol/lit) -0.75
the rate expression for the given reaction is,
-rN2O = 0.2046 (C N2O)1.75
Last Modified on: 30-Apr-2024
Chemical Engineering Learning Resources - msubbu
e-mail: learn[AT]msubbu.academy
www.msubbu.in