The gas phase decomposition of A takes place according to the irreversible reaction, A → 3P. The kinetics of the reaction was studied by measuring the increase in pressure in a constant volume reaction vessel. At 504oC and an initial pressure of 312 mm Hg, the following data were obtained:
Time (Sec) 390 777 1195 3155 ∞ Total pressure (mm Hg) 408 488 562 779 931
Calculations:
Total pressure of the system (π) and partial pressure of A (pA) are related as:
pA = pAo - (a/Δn)(π - πo)
where, πo is the initial pressure of the system;
pAo is the initial pressure of A;
a is the stoichiometric coefficient of A;
and Δn = stoichiometric coefficient of products minus reactants.
For the given problem, πo = pAo = 312 mm Hg (Assuming feed is pure A)
a = 1
Δn = 3-1 = 2
pA = 312 - (1/2)(π - 312)
i.e.,
pA = 312 - 0.5 (p - 312)
pA for various times are calculated as follows:
Time (Sec) 390 777 1195 3155 ∞ Total pressure (mm Hg) 408 488 562 779 931 pA (mm Hg) 264 224 187 78.5 2.5
Fractional conversion of A is given by:
XA = (pAo - pA) / pAo
For various time values, XA and -ln(1- XA) is calculated and tabulated as follows:
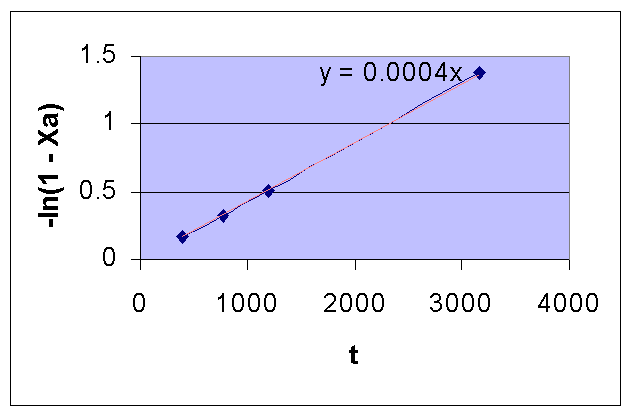
Time (Sec) 390 777 1195 3155 ∞ pA (mm Hg) 264 224 187 78.5 2.5 XA 0.154 0.282 0.401 0.748 0.992 -ln(1 - XA) 0.167 0.331 0.512 1.378 4.828
For a first order reaction, a plot of t Vs. -ln(1 - XA) in a linear XY graph is a straight line with a slope of k.
From the following plot, it is seen that the given data is for a first order reaction.

Last Modified on: 30-Apr-2024
Chemical Engineering Learning Resources - msubbu
e-mail: learn[AT]msubbu.academy
www.msubbu.in