The decomposition of NO2 follows a second order rate equation. Data at different temperatures are as follows:
T (K) 592 603 627 651.5 656 k (cm3/gmol.sec) 522 755 1700 4020 5030
Compute the energy of activation Energy from the data. The reaction is 2NO2 → 2NO + O2
Calculations:
Activation energy is found from the Arrhenius' relation
k = ko e-E/RT
i.e.,
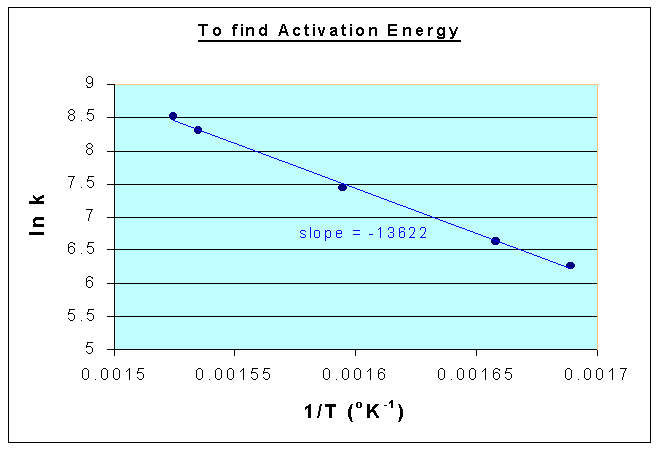
ln k vs. 1/T is a straight line with a slope of -E/R
where, E is the activation energy; and
R is the universal gas constant.
|
T (K) |
592 |
603 |
627 |
651.5 |
656 |
|
k (cm3/gmol.sec) |
522 |
755 |
1700 |
4020 |
5030 |
|
1/T (oK-1) |
0.001689 |
0.001658 |
0.001595 |
0.001535 |
0.001524 |
|
ln k |
6.257668 |
6.626718 |
7.438384 |
8.299037 |
8.523175 |
From the above data, the following graph is drawn, and the slope is = -13622

Therefore,
E/R = 13622
E
= 13622 x 8314 = 113253.3 kJ/kmolLast Modified on: 30-Apr-2024
Chemical Engineering Learning Resources - msubbu
e-mail: learn[AT]msubbu.academy
www.msubbu.in