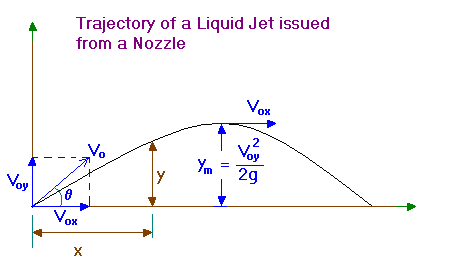
In a free jet the pressure is atmospheric throughout the trajectory.

Vox = Vo cosq = constant = Vx
Voy = Vo sinq
x = Vox t
y = Voy t – gt2/2
eliminating t gives,
y = x Voy/Vox – gx2/(2Vox2)
i.e,
y = x tanq – gx2/(2Vo2 cos2q)
This is the equation of the trajectory.
---------------
At the point of maximum elevation, Vy = 0 and application of Bernoulli’s law between the issue point of jet and the maximum elevation level,
Vo2/(2g) = Vox2/(2g) + ym
Since, Vo2/(2g) = Vox2/(2g) + Voy2/(2g)
we get,
ym = Voy2/(2g)
Last Modified on: 14-Sep-2014
Chemical Engineering Learning Resources - msubbu
e-mail: msubbu.in[AT]gmail.com
Web: http://www.msubbu.in