Thermodynamics - GATE-CH Questions
Home -> GATE Questions with Solutions at MSubbu.Academy -> Thermodynamics->
Basic Concepts
GATE-CH-2002-2-22-td-2mark
A rigid vessel, containing three moles of nitrogen gas at 30oC , is heated to 250oC . Assume the average heat capacities of nitrogen to be \(C_P = 29.1\) J/mol.oC and \(C_V = 20.8\) J/mol.oC . The heat required, neglecting the heat capacity of the vessel, is
GATE-CH-2003-8-td-1mark
One mole of Nitrogen at 8 bar and 600 K is contained in a piston-cylinder arrangement. It is brought to 1 bar isothermally against a resisting pressure of 1 bar. The work done (in Joule) by the gas is
GATE-CH-2006-31-td-2mark
Match the following:
| (A) Heat |
(I) State function |
| (B) Internal energy |
(II) Path function |
| (C) Work |
|
| (D) Entropy |
|
GATE-CH-2010-17-td-1mark
A new linear temperature scale, denoted by \(^\circ \)S, has been developed, where the freezing point of water is 200\(^\circ \)S and the boiling point is 400\(^\circ \)S. On this scale, 500\(^\circ \)S corresponds, in degrees Celsius to
GATE-XE-2008-G-3-td-1mark
The densities of water and ice at 0oC are 1000 kg/m3 and 900 kg/m3, respectively. If ice at 0oC is allowed to melt into water at the same temperature, then
[Index]
GATE-XE-2009-E-5-td-1mark
An ideal gas undergoes expansion according to the process \(PV^{0.5} = \text {constant}\). The temperature of the gas during the expansion process
GATE-XE-2012-E-1-td-1mark
Consider a piston-cylinder arrangement containing a gas. This system is heated by placing it on the top of a burner. The system undergoes
GATE-XE-2014-E-2-td-1mark
A small container has gas at high pressure. It is placed in an evacuated space. If the container is punctured, work done by the gas is
GATE-CH-1994-3-p-td-1mark
Pressure is an extensive property. (True/False)
GATE-CH-1994-3-q-td-1mark
Work done by a gas during free expansion is zero. (True/False)
[Index]
GATE-CH-1994-3-s-td-1mark
The mechanical work done by a system is always equal to \(\int P dV\). (True/False)
GATE-CH-2003-43-td-2mark
Heat capacity of air can be approximately expressed as \(C_P = 26.693 + 7.365 \times 10^{-3}T\) where \(C_P\) is in J/(mol.K) and \(T\) is in K. The heat given off by 1 mole of air when cooled at 1 atmospheric pressure from 500oC to -100oC is
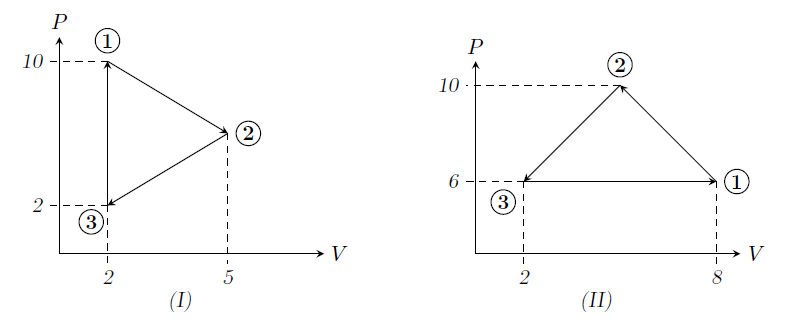
GATE-XE-2008-G-13-td-2mark
Consider the cycles given below and state which one of the following statement is true.
GATE-CH-2013-35-td-2mark
Calculate the heat required (in kJ, up to 1 digit after the decimal point) to raise the temperature of 1 mole of a solid material from 100oC to 1000oC . The specific heat \((C_P)\) of the material (in J/mol.K) is expressed as \(C_P = 20 + 0.005T\), where \(T\) is in K. Assume no phase change. ____________
GATE-XE-2012-E-21-22-td-4mark
A piston-cylinder arrangement as shown in the figure initially contains air at 150 kPa and 400oC. The arrangement is allowed to cool to the ambient temperature of 20oC. The characteristic gas constant for air is 0.287 kJ/kg.K. The cylinder wall has stops of negligible thickness that can prevent the piston from moving down. The stops are 1 m from the inner side of the base surface of the cylinder. At the initial state, the piston is resting 1 m above the stops.

(i) The final pressure in the cylinder (in kPa) is
{#1}
(ii) The specific work done by the air (in kJ/kg) during the process is
{#2}
Solution
GATE-CH-1990-6-iii-td-2mark
The maximum work obtainable from a closed system under isothermal operation is given by --------------- ; For one mole of an ideal gas expanding isothermally to twice its volume, this is equal to --------------- .
GATE-CH-1990-6-iv-td-2mark
The minimum work required for steady isothermal compression of a real gas is given by --------------- ; For one mole of an ideal gas that is compressed isothermally from one to two atmospheres, this is equal to --------------- .
[Index]
Last Modified on: 04-May-2024
Chemical Engineering Learning Resources - msubbu
e-mail: learn[AT]msubbu.academy
www.msubbu.in

