Mass Transfer - GATE-CH Questions
Home -> GATE Questions with Solutions at MSubbu.Academy -> Mass Transfer->
Extraction
GATE-CH-2006-14-mt-1mark
An ideal single stage extraction process is used to treat 100 mol/s of an organic feed solution. The solute concentration in this solution is to be reduced from 0.5 mol% to 0.1 mol%. A pure solvent \(S\) is used. To reduce the solvent requirement by half for the same separation,
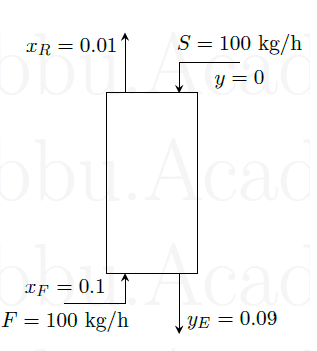
GATE-CH-2008-8-mt-1mark
For a system containing species \(P\), \(Q\) and \(R\), composition at point \(k\) on the ternary plot is
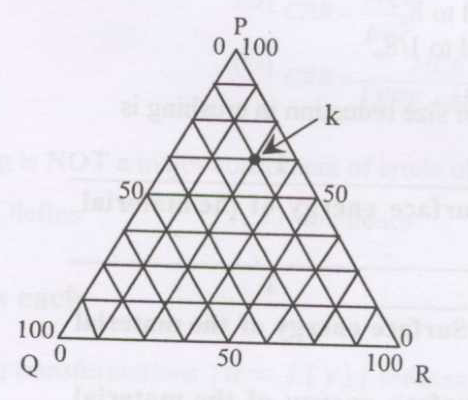
GATE-CH-2017-14-mt-1mark
Which of the following conditions are valid at the plait point?
- [P)] Density difference between the extract and raffinate phases is zero
- [Q)] Interfacial tension between the extract and raffinate phases is zero
- [R)] Composition difference between the extract and raffinate phases is zero
GATE-CH-1987-15-ii-mt-2mark
Acetone from 1 kg of an aqueous solution containing 20% acetone (by weight) is to be extracted using 1 kg of an organic solvent trichloroethane. Trichloroethane and water are immiscible. The distribution coefficient, \[ \frac {\text {kg acetone}}{\text {kg trichloroethane}} = 1.65\; \frac {\text {kg acetone}}{\text {kg water}} \] Estimate the amounts of acetone (kg) in (i) extract phase and (ii) aqueous phase at equilibrium.
(i) ____________
{#1}
(ii) ____________
{#2}
GATE-CH-2006-76-77-mt-4mark
Solvent \(C\) is used to extract solute \(B\) selectively from, 100 kg/h feed mixture \(A+B\) in a steady state continuous process shown below. The solubility of \(C\) in the raffinate and the solubility of \(A\) in the extract are negligible. The extract is distilled to recover \(B\) in the bottom product. The overhead product is recycled to the extractor. The loss of solvent in the bottoms is compensated by make up solvent \(S_d\). The total flow rate of the solvent stream \(S\) going to the extractor is 50 kg/h. The mass fractions (\(X_i\)’s) of some selected streams are indicated in the figure below.

(i) Distillation bottoms flow rate W and solvent dosing rate \(S_d\) in kg/h are
{#1}
(ii) Feed rate \(E\) to the distillation column and overhead product rate \(T\) in kg/h are
{#2}
[Index]
GATE-CH-2012-48-49-mt-4mark
A counter-current extraction column is designed to remove 99% of solute \(C\) from a solution of solvent \(A\) and solute \(C\) using pure solvent \(B\). The initial concentration of solute in the solution of \(A+C\) is 20 wt%, and the total flow of solution is 1000 kg/h. If the equilibrium relationship is \(Y=0.5X\), where \(Y\) = mass of \(C\)/mass of \(B\), and \(X\) = mass of \(C\)/mass of \(A\).
(i) The minimum flow rate of solvent \(B\) required (in kg/h) is
{#1}
(ii) If the flow rate of \(B\) is 2400 kg/h, then the theoretical number of stages in the column, using Kremser’s equation (adjusted to the next integer) is
{#2}
GATE-CH-2001-2-14-mt-2mark
In a single stage extraction process, 10 kg of pure solvent \(S\) (containing no solute \(A\)) is mixed with 30 kg of feed \(F\) containing \(A\) at a mass fraction \(x_F\) = 0.2. The mixture splits into an extract phase \(E\) and a raffinate phase \(R\), containing \(A\) at \(x_E=0.5\) and \(x_R=0.05\), respectively. The total mass of the extract phase is (in kg)
GATE-CH-2004-66-mt-2mark
In liquid-liquid extraction 10 kg of a solution containing 2 kg of solute \(C\) and 8 kg of solvent \(A\) is brought into contact with 10 kg of solvent \(B\). Solvents \(A\) and \(B\) are completely immiscible in each other whereas solute \(C\) is soluble in both the solvents. The extraction process attains equilibrium. The equilibrium relationship between the two phases is \(Y^* = 0.9X\) where \(Y^*\) is kg of \(C\)/kg of \(B\) and \(X\) is kg of \(C\)/kg of \(A\). Choose the correct answer
GATE-CH-2005-42-mt-2mark
In the triangular diagram represented below for a batch separation process, a stream \(F\) is mixed with a solvent \(B\) to produce products \(R\) and \(E\). Substance \(A\) is the carrier liquid and \(C\) is the solute to be extracted. The amounts of \(B\) and \(E\) are 1 kg and 1.20 kg respectively. The length \(FM\) is 3.1 and length \(FB\) is 8.5 units on the figure. The ratio \(R/E\) is estimated to be
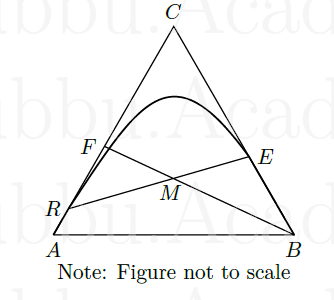
GATE-CH-2007-50-mt-2mark
It is desired to reduce the concentration of pyridine in 500 kg of aqueous solution from 20 weight percent to 5 weight percent in a single batch extraction using chloro-benzene as solvent. Equilibrium compositions (end points of the tie line) in terms of weight percent of pyridine-water-chlorobenzene are (5, 95, 0) and (11, 0, 89). The amount of pure solvent required in kg for the operation is
[Index]
GATE-CH-2008-54-mt-2mark
A feed (\(F\)) containing a solute is contacted with a solvent (\(S\)) in an ideal stage as shown in the diagram below. Only the solute transfers into the solvent. The flow rates of all the streams are shown on a solute free basis and indicated by the subscript \(S\). The compositions of the streams are expressed on a mole ratio basis. The extract leaving the contactor is divided into two equal parts, one part collected as the product (\(P\)) and the other stream is recycled to join the solvent. The equilibrium relationship is \[ Y^* = 2X \] The product flow rate (\(P_s\)) and composition (\(Y_{\text {out}}\)) are
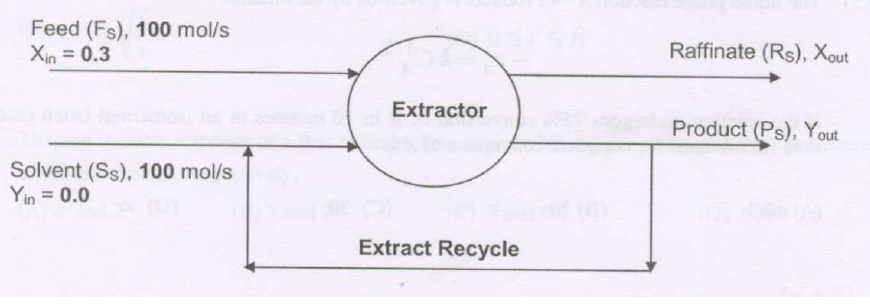
GATE-CH-2016-44-mt-2mark
Solute \(C\) is extracted in a batch process from its homogeneous solution of \(A\) and \(C\), using solvent \(B\). The combined composition of the feed and the extracting solvent is shown in the figure below as point \(M\), along with the tie line passing through it. The ends of the tie line are on the equilibrium curve.
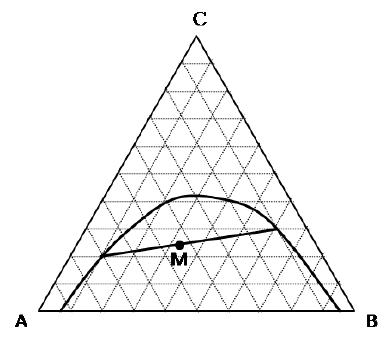
What is the selectivity for \(C\) ?
GATE-CH-1996-22-mt-5mark
990 kg/h of an aqueous solution has a solute at a concentration of 0.1 kg solute/ kg water. It is treated with 600 kg/h of a pure immiscible organic solvent in a 2-stage mixer-settler system. If the organic and aqueous streams leaving each stage are in equilibrium such that \[\left(\frac{\text{kg solute in organic phase}}{\text{kg solvent}}\right) = 2 \left(\frac{\text{kg solute in aqueous phase}}{\text{kg water}}\right)\] calculate the kg solute extracted per kg solvent if countercurrent operation is employed.
GATE-CH-2000-10-mt-5mark
A continuous-contact extraction column is used to extract a solute from an aqueous stream (\(F\)) using an organic solvent (\(S\)). The distribution coefficient (\(y/x\)) is 1.0, where \(x\) and \(y\) are the mass fractions of solute in raffinate and extract phases, respectively. The height of transfer unit based on the extract phase is 1.0 m. The rest of the data are given in the figure. Assuming that the phase flow rates are constant, find the height of the tower (in m).
GATE-CH-1995-3-d-mt-2mark
Match the following:
[Index]
GATE-CH-1991-16-ii-mt-8mark
An aqueous solution containing 1.5 kmol of solute/m\(^3\) is fed at 36 mL/s to the top of the packed column of height 1.6 m and cross sectional area of 0.0045 m\(^2\) and it leaves at the bottom with 1.4 kmol/m\(^3\). An organic solvent, \(B\), containing 0.008 kmol of solute/m\(^3\) flows counter to the aqueous phase at 9 mL/s. The equilibrium relationship is \[ y^* = 0.3 x \] where \(y\) is the concentration of solute in solvent rich phase; and \(x\) is that of in aqueous phase.
Determine:
(a) the log mean concentration difference for the transfer (in mole fraction).
{#1}
(b) the overall volumetric transfer coefficient (in s\(^{-1}\)), based on the organic phase. ____________\(\times 10^{-3}\)
{#2}
(c) the height of transfer unit (in m).
{#3}
GATE-CH-1993-23-mt-5mark
A mineral containing 20% elemental sulfur is to be leached with hot gas oil in which sulfur is soluble to the extent of 10 parts in 100 parts of oil by weight. The oil is recycled over the batch of ground mineral till no further dissolution of sulfur takes place. On drainage, the solid minerals retain the solution to the extent of one-tenth the weight of undissolved solid (sulfur and gauge). No preferential adsorption takes place. Calculate the equilibrium compositions and quantities of the solid and liquid phases if 50 kg of oil is used for leaching 100 kg of fresh mineral.
GATE-CH-2002-14-mt-5mark
It is desired to extract acetone from a feed containing acetone and water, using chloroform as the solvent, in two cross current extraction stages as shown below:

Assume that water and chloroform are immiscible. The following data are given for the process:
-
The feed is an equimolar mixture of acetone and water.
-
The quantities of chloroform used in the two stages are equal.
-
60 mole % of the acetone in the feed is extracted in stage I.
-
The extract and raffinate phases exiting from each stage are in equilibrium. The equilibrium relation for the distribution of the acetone is given by
\[\frac{\text{Moles of acetone in water-rich phase}}{\text{Moles of water in water-rich phase}} = 2 \times \frac{\text{Moles of acetone in chloroform-rich phase}}{\text{Moles of chloroform in chloroform-rich phase}}\]
-
Indicate (with the help of the above diagram) the components in each stream.
-
Determine the quantity of chloroform used in each stage per mole of feed.
-
Determine the mole fraction of acetone in final product stream.
[Index]
Last Modified on: 03-May-2024
Chemical Engineering Learning Resources - msubbu
e-mail: learn[AT]msubbu.academy
www.msubbu.in






